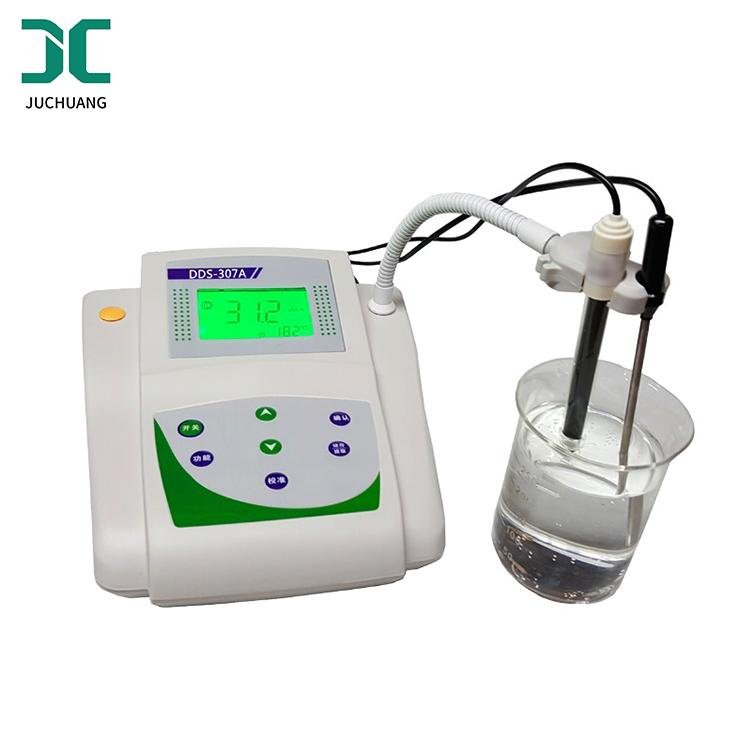
Conductivity, a physical concept, means that the product of this quantity and the electric field strength in the medium is equal to the conduction current density, which can also be called conductivity. For isotropic media, conductivity is a scalar; for anisotropic media, conductivity is a tensor. In ecology, conductivity is a numerical representation of the ability of a solution to conduct electrical current. The unit is expressed in Siemens per meter (S/m). The method of this instrument to test the conductance is to apply the AC voltage generated by the oscillator to the electrode (the purpose of adding the AC voltage is to avoid the polarization of the electrode), and a current is generated in the conductivity cell, which is related to the conductivity of the tested solution. It is proportional to the current-voltage conversion, amplification, detection, converted into DC voltage, through temperature compensation, etc., and finally converted into a digital signal by the A/D converter, which is displayed by a microcomputer. The whole process is controlled and processed by a microcomputer. The instrument is widely used in scientific research, teaching, industry, agriculture and many other disciplines and fields.