| Model: | - |
|---|---|
| Brand: | - |
| Origin: | - |
| Category: | Chemicals / Organic Chemical Materials / Pharmaceutical Chemicals |
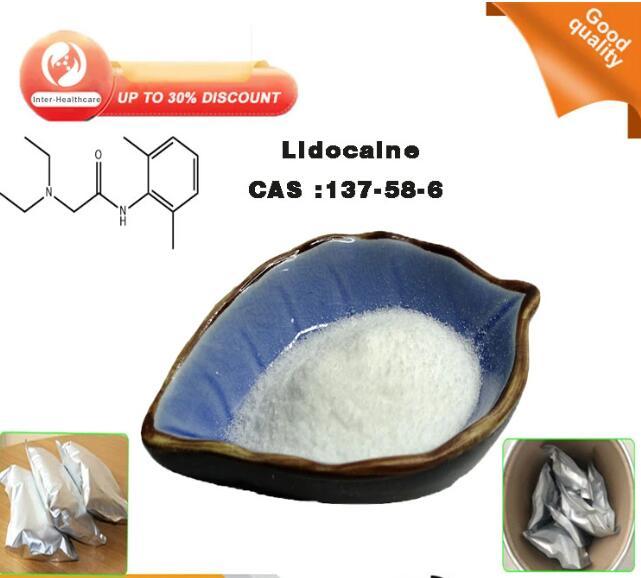
| Label: | Lidocaine , 137-58-6 |
| Price: |
US $220
/ kg
|
| Min. Order: | 1 kg |
Product Description
Lidocaine is a synthetic organic compound characterized by its amide structure, primarily composed of an aromatic ring linked to an aminoethyl chain. It is a white, crystalline powder that is soluble in alcohol, ether, and benzene. In the research settings, it serves as a standard agent in studies exploring the mechanisms of sodium channel function due to its ability to bind to specific sites within these channels. Lidocaine in electrophysiological experiments are used to understand the gating properties of sodium channels and to map their role in the generation and conduction of electrical signals in various cell types. The compound′s impact on these ion channels has made it a subject of interest in the field of neurobiology, where it is used to elucidate the fundamental processes underlying neuronal excitability and conduction.
| Payment Terms: | Bitcoin, Western Union,T/T |
|---|---|
Member Information
| Shijiazhuang Fansheng Technology Co., Ltd. | |
|---|---|
| Country/Region: | He Bei - China |
| Business Nature: | Manufacturer |
| Phone: | 13731105996 |
| Contact: | Lee (Export Manager) |
| Last Online: | 04 Mar, 2024 |
Related Products of this Company
-
GBL Gamma-Butyrolactone γ-butyrolactone
US $150
-
CAS No. 38304-91-5 Hair Care Raw Powder
US $270
-
Hair Growth Minoxidil CAS 38304-91-5
US $220
-
DL-Menthol CAS 89-78-1
US $470
-
Peptides Tirzepatide 10mg/vial GLP-1
US $100
-
IGF-1 LR3 LR3-IGF1 CAS 946870-92-4
US $110
-
GBL Gamma-Butyrolactone γ-butyrolactone
-
Pregabalin powder CAS 148553-50-8
US $150
-
10MG vial pack Semaglutide 99%
US $100
-
HCG Human Chorionic Gonadotropin CAS
US $75