| Model: | customized |
|---|---|
| Brand: | Ferrotec |
| Origin: | Made In China |
| Category: | Electronics & Electricity / Insulation Material |
| Label: | DBC substrates , CPV , Electronic component |
| Price: |
US $0.08
/ cm²
|
| Min. Order: | 200 cm² |
Product Description
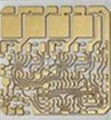
The DBC substrates basis is a ceramic isolator (currently aluminium oxide or aluminum nitride),to which pure copper is applied in a high-temperature melting and diffusion process, and which is then connected adhesively to the ceramics. This gives rise to the name “Direct Bonded Copper”
In particular the great heat conductivity (up to 180W/mK) and high capacity and spread of the thick copper coating (200-600um)make DBC substrates indispensable in high performance electronics.
Using the purest of copper makes for a unique current carrying capacity as compared to alternative technologies. Another reason for this is the low mechanical load of the uncased silicon chips, which have a similar thermal expansion as DBC substrates.
For about ten years, this DBC technology has been used for high performance cooling devices as well. As its heart is a channel structure made of thin copper foils, which are assembled into a hermetically tight block in the bonding process. This creates a strongly enlarged copper surface, enabling efficient liquid cooling.
Particularly effective cooling is achieved by a combination of DBC substrates with a cooling channel structure, where direct contact of the uncased power chips and the water-cooled basis plate is possible.
Member Information
| Shanghai Shenhe Thermo-Magnetics Electronics Co.,LTD | |
|---|---|
| Country/Region: | Shang Hai - China |
| Business Nature: | Manufacturer |
| Phone: | 13524566884 |
| Contact: | Susan (Overseas sales) |
| Last Online: | 12 Mar, 2012 |
Related Products of this Company
-
DBC substrate-1
US $0.08
-
DBC substrate
US $0.08
-
AL2O3 DBC substrate-4
US $1